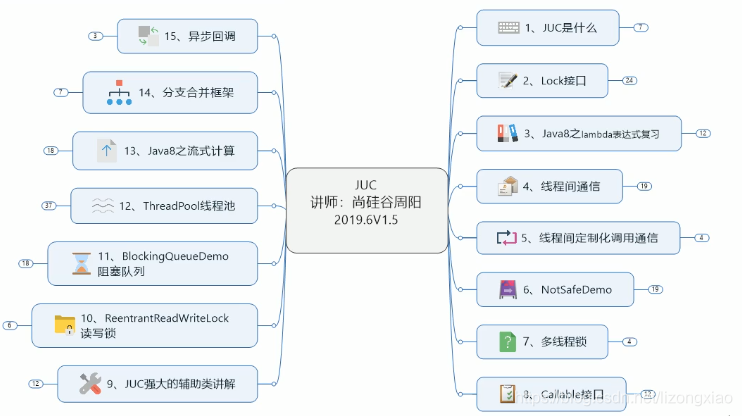
JUC学习
JUC学习
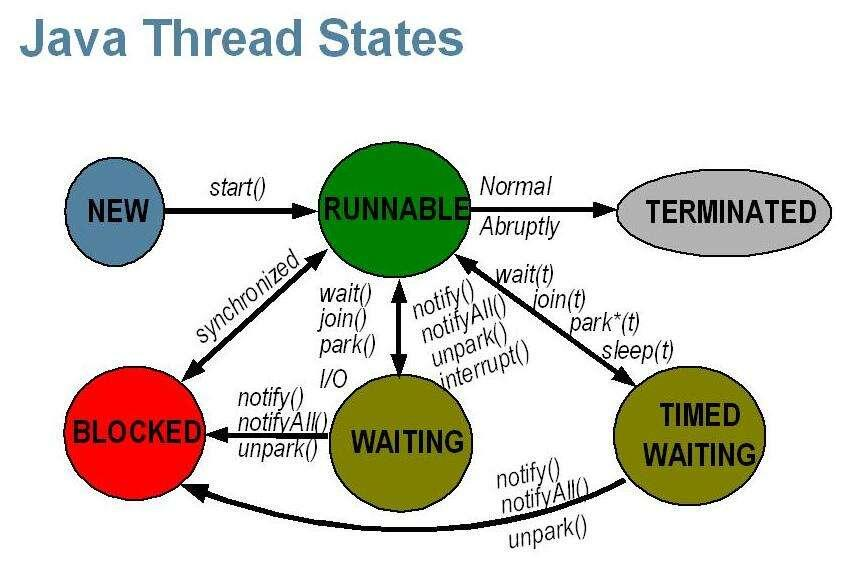
线程的六种状态 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public enum State NEW, RUNNABLE, BLOCK, WAITING, TIME_WAITING, TERMINATED; }
Lambda Express 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1. 拷贝小括号,写死右箭头,落地大括号;() ->{sout};2. @FunctionalInterface 3. default 4. 静态方法实现
Condition 精准顺序访问控制(自己上锁) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 class ShareData private int number = 1 ; private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); private Condition c1 = lock.newCondition(); private Condition c2 = lock.newCondition(); private Condition c3 = lock.newCondition(); public void printc1 () lock.lock(); try { while (number != 1 ){ c1.await(); } for (int i = 1 ; i <= 5 ; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t" +i); } number = 2 ; c2.signal(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public void printc2 () lock.lock(); try { while (number != 2 ){ c2.await(); } for (int i = 1 ; i <= 10 ; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t" +i); } number = 3 ; c3.signal(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public void printc3 () lock.lock(); try { while (number != 3 ){ c3.await(); } for (int i = 1 ; i <= 15 ; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t" +i); } number = 1 ; c1.signal(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } } public class ConditionDemo public static void main (String[] args) ShareData shareData = new ShareData(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 1 ; i <= 10 ; i++) { shareData.printc1(); } },"A" ).start(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 1 ; i <= 10 ; i++) { shareData.printc2(); } },"B" ).start(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 1 ; i <= 10 ; i++) { shareData.printc3(); } },"C" ).start(); } }
八🔒理论 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 class Phone public static synchronized void sendEmail () throws Exception try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("*******sendEmail" ); } public synchronized void sendMs () throws Exception TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2 ); System.out.println("*******sendMs" ); } public void sayHello () throws Exception TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3 ); System.out.println("*****sayHello" ); } } public class LockBDemo05 public static void main (String[] args) throws InterruptedException Phone phone = new Phone(); Phone phone2 = new Phone(); new Thread(()->{ try { phone.sendEmail(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },"A" ).start(); Thread.sleep(100 ); new Thread(()->{ try { phone.sendMs(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },"B" ).start(); Thread.sleep(100 ); new Thread(()->{ try { phone.sayHello(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },"c" ).start(); } }
静态同步方法锁的是.class 是类的模板(和锁this不一样)
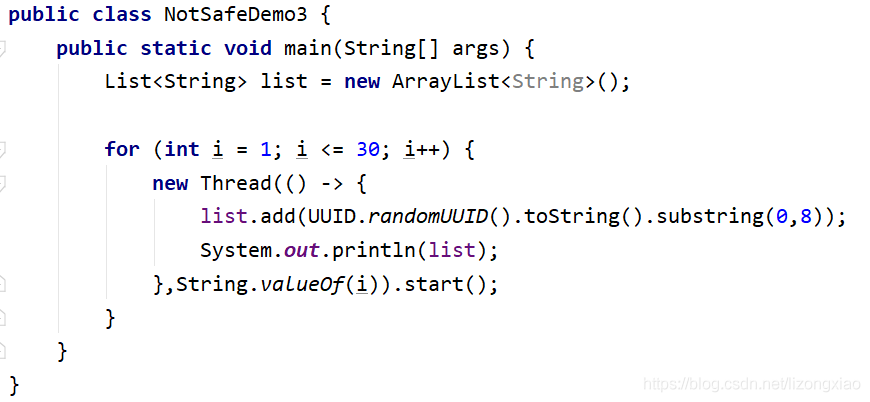
并发集合 集合是不安全的CopyOnWriteArrayList()
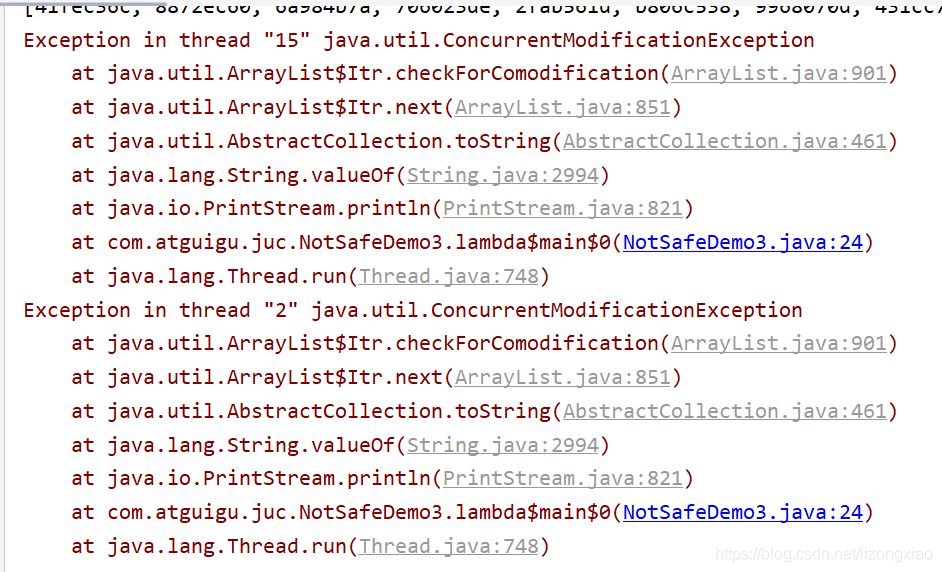
并发修改异常
解决办法new Vector<>(); Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList()); new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>(); //写时复制(底层用的unlock)
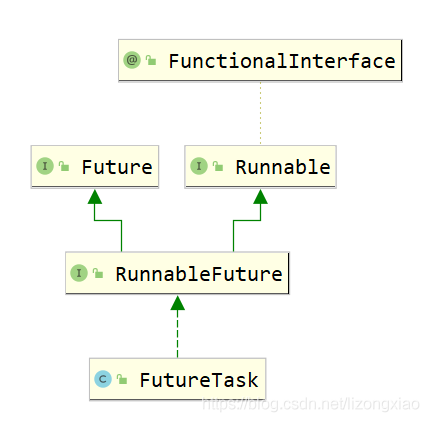
不安全Set 解决CopyOnWriteArraySet<>(); 不安全Map 解决ConcurrentHashMap<>(); 第三种多线程方法Callable 思想:new Thread 需要传入一个runnable接口,找runnable接口实现子类,FutureTask既实现了runnable又实现callable接口
辅助工具类 CountDownLatchDemo(减法) 保证一组子线程全部执行完毕之后再进行主线程的执行操作
CyclicBarrierDemo (加法) 每运行多少次子线程运行一次CyclicBarrierDemo线程
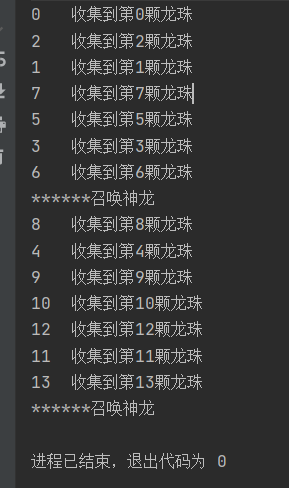
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 package com.demo;import java.util.concurrent.BrokenBarrierException;import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;public class cyclicBarrierDemo public static void main (String[] args) CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(7 ,()->{ System.out.println("******召唤神龙" ); }); for (int i = 0 ; i <14 ; i++) { int finalI = i; new Thread(()->{ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t收集到第" + finalI +"颗龙珠" ); try { cyclicBarrier.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (BrokenBarrierException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } },String.valueOf(i)).start(); } } }
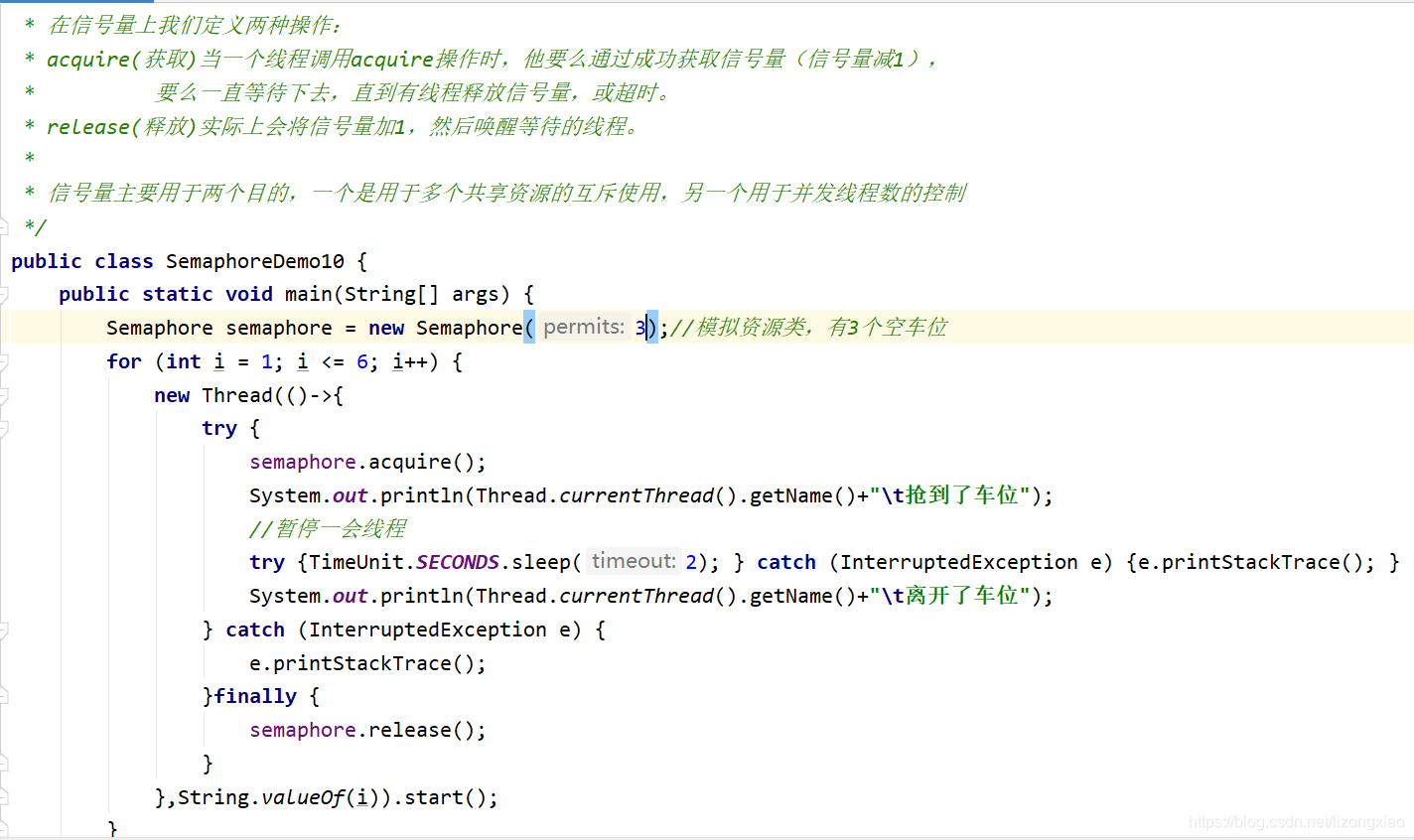
Semaphore信号量
ReadWriteLock读写锁
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 class MyCache private volatile Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); private ReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); public void put (String key, Object value) readWriteLock.writeLock().lock(); try { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t--写入数据" + key); try { TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.sleep(300 ); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } map.put(key, value); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t--写入完成" ); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock(); } } public void get (String key) readWriteLock.readLock().lock(); try { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t读取数据" ); Object result = map.get(key); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t读取完成" + result); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { readWriteLock.readLock().unlock(); } } } public class ReadWriteLockDemo11 public static void main (String[] args) MyCache myCache = new MyCache(); for (int i = 1 ; i <= 5 ; i++) { final int tempInt = i; new Thread(()->{ myCache.put(tempInt+"" ,tempInt+"" ); },String.valueOf(i)).start(); } for (int i = 1 ; i <= 5 ; i++) { final int tempInt = i; new Thread(()->{ myCache.get(tempInt+"" ); },String.valueOf(i)).start(); } } }
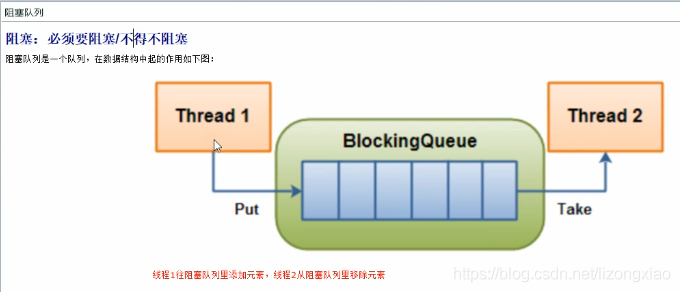
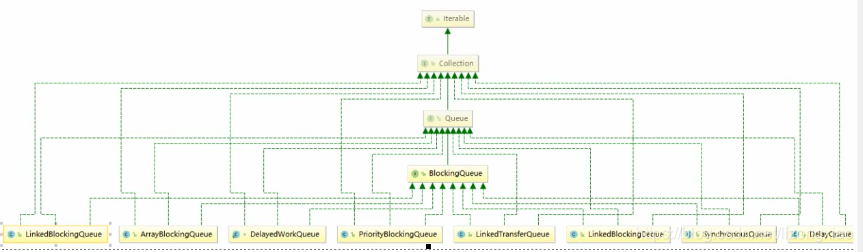
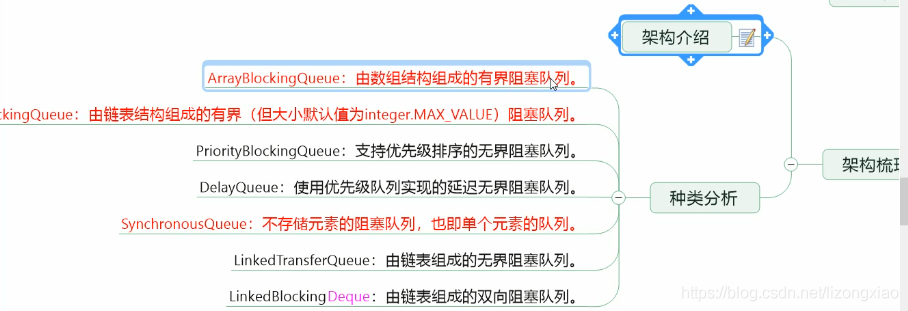
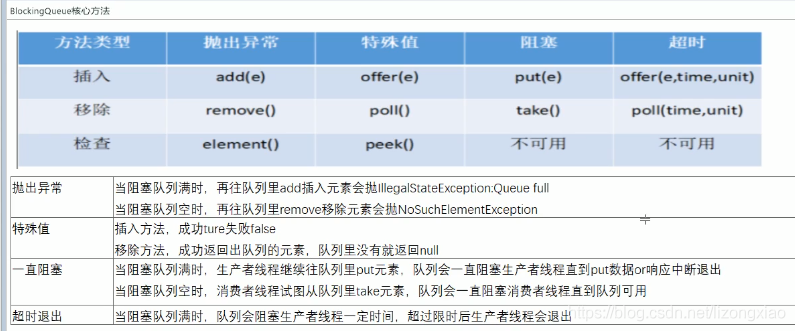
7种BlockingQueue阻塞队列
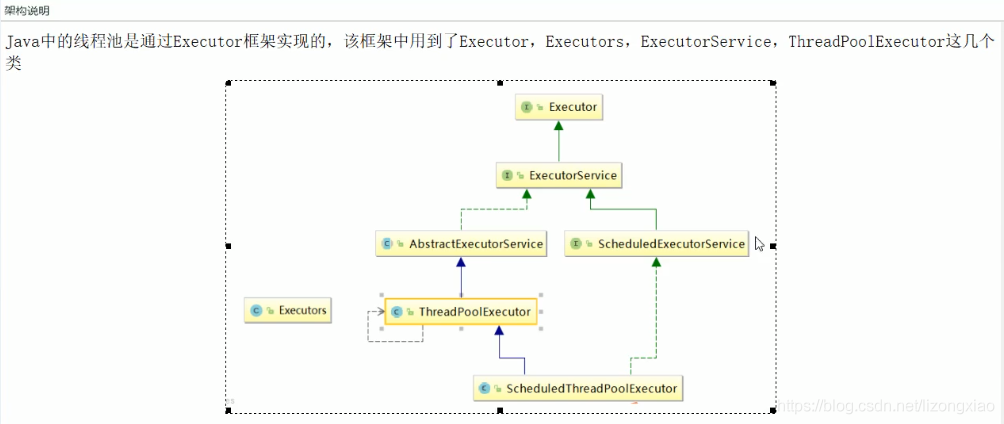
线程池
线程池的三大方法
ExecutorService threadpool = Executors.newFixedThreadpool(n);
//执行长期任务性能好,创建一个线程池,一池有N个固定线程,有固定的线程数
newSingleThreadExecutor();//一个任务一个任务的执行,一池一线程
newCacheThreadPool()
//执行很多短期异步任务,线程池根据需要创建新线程,
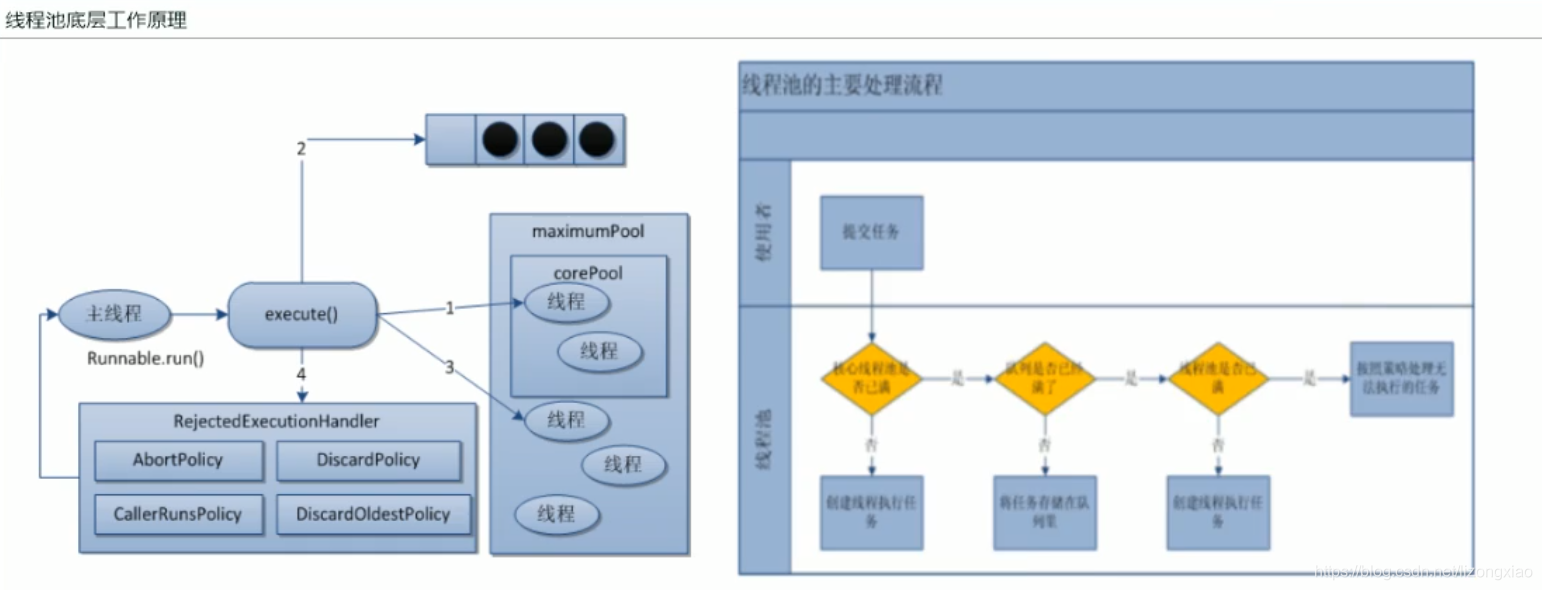
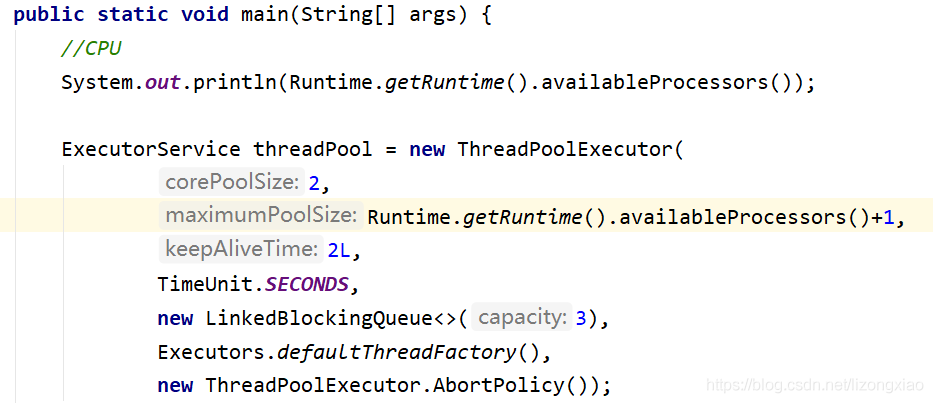
ThreadPoolExecutor底层原理 线程池的7大参数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public ThreadPoolExecutor (int corePoolSize,//常驻核心线程数 int maximumPoolSize,//线程池中能够容纳同时执行的最大线程数,必须大于等于1 long keepAliveTime,//多余线程存活时间 TimeUnit unit,//keepAliveTime的时间单位 BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,//阻塞任务队列,被提交但未执行的任务 ThreadFactory threadFactory,//生成工厂 一般用默认 RejectedExecutionHandler handler) }
线程池底层运行原理
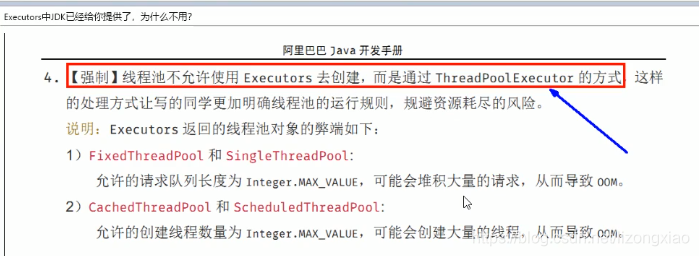
实际工作中只用自定义的线程池,不能用JDK的(防止内存被挤爆、资源耗尽)
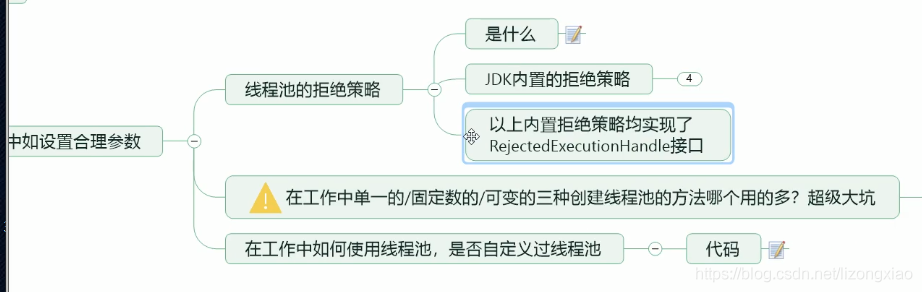
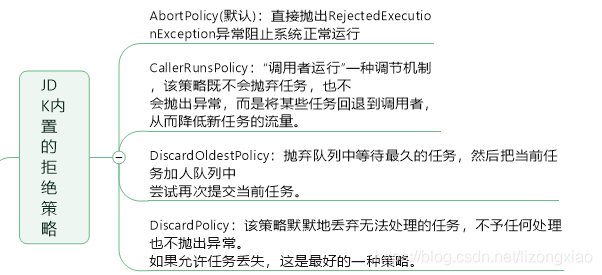
线程池的拒绝策略
1 2 System .Runtime .Runtime() .availableProcessors() );
cup 密集型 几核就是几 保存 cup 运行最高效率
Io 密集型 判断程序十分耗 io 的线程 线程大于 2 倍
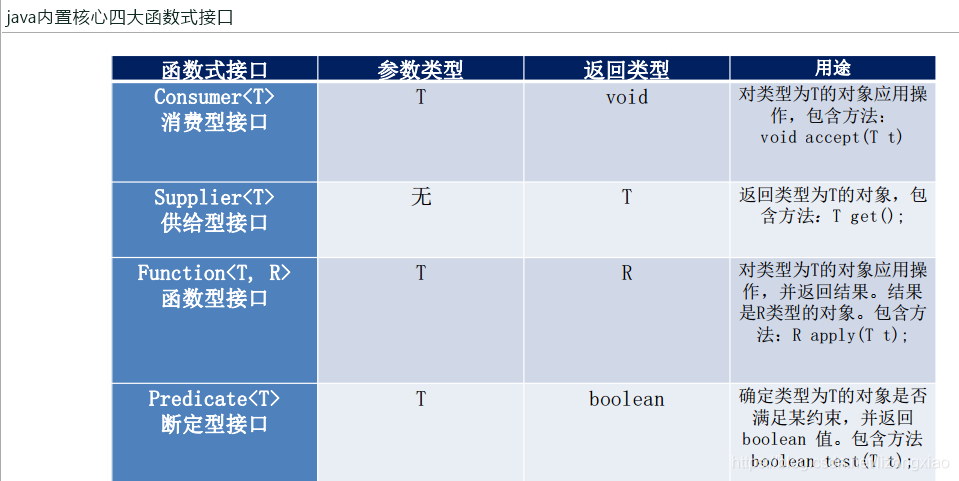
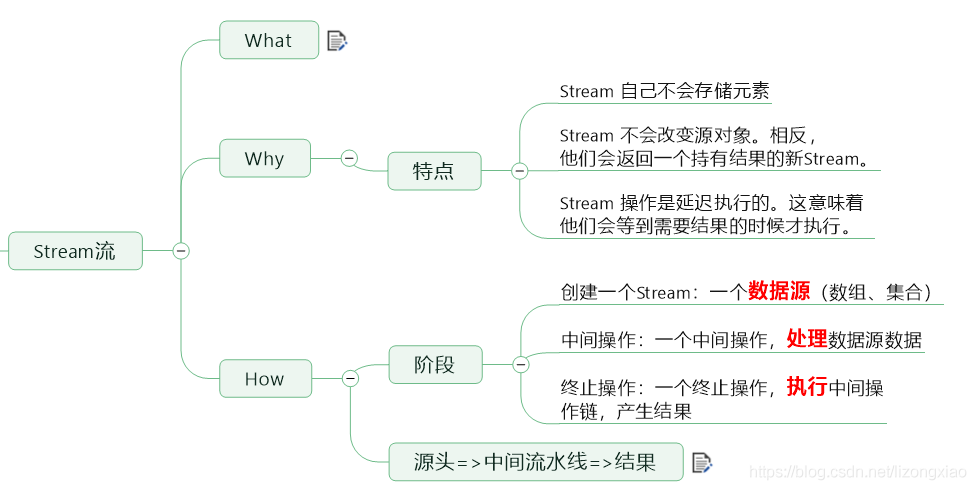
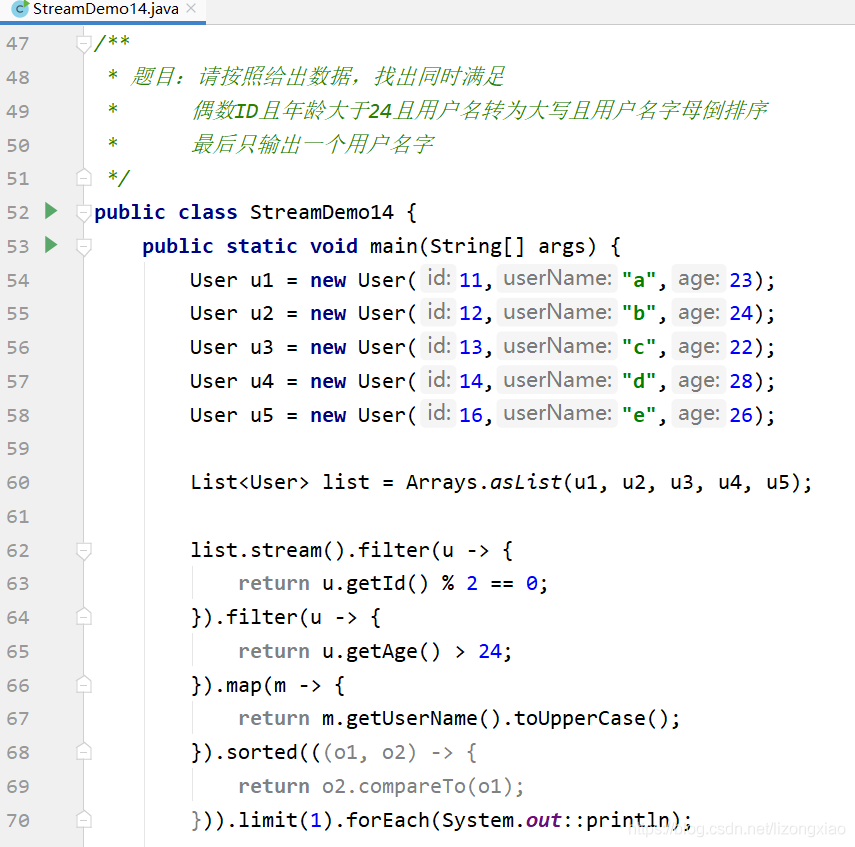
JUF四大函数式接口 Stream流式计算
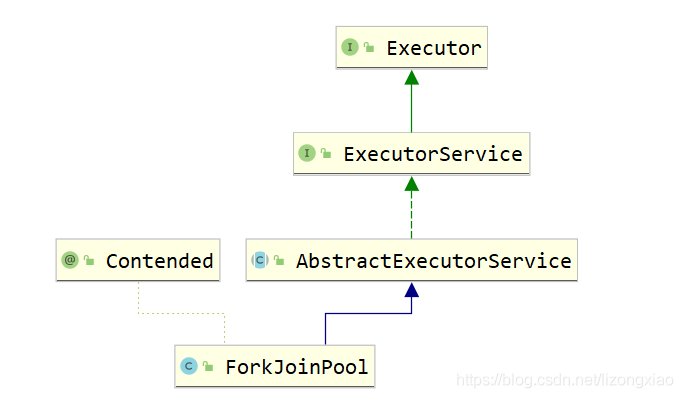
ForkJoinPool分支合并框架 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 package com.atguigu.juc2;import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool;import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinTask;import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask;class MyTask extends RecursiveTask <Integer > private static final Integer ADJUST_VALUE = 10 ; private int begin; private int end; private int result; public MyTask (int begin, int end) this .begin = begin; this .end = end; } @Override protected Integer compute () if ((end - begin) <= ADJUST_VALUE) { for (int i = begin; i <= end; i++) { result = result + i; } } else { int middle = (end + begin) / 2 ; MyTask task01 = new MyTask(begin, middle); MyTask task02 = new MyTask(middle + 1 , end); task01.fork(); task02.fork(); result = task01.join() + task02.join(); } return result; } } public class ForkJoinDemo15 public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception MyTask myTask = new MyTask(0 , 100 ); ForkJoinPool threadPool = new ForkJoinPool(); ForkJoinTask<Integer> forkJoinTask = threadPool.submit(myTask); System.out.println(forkJoinTask.get()); threadPool.shutdown(); } }
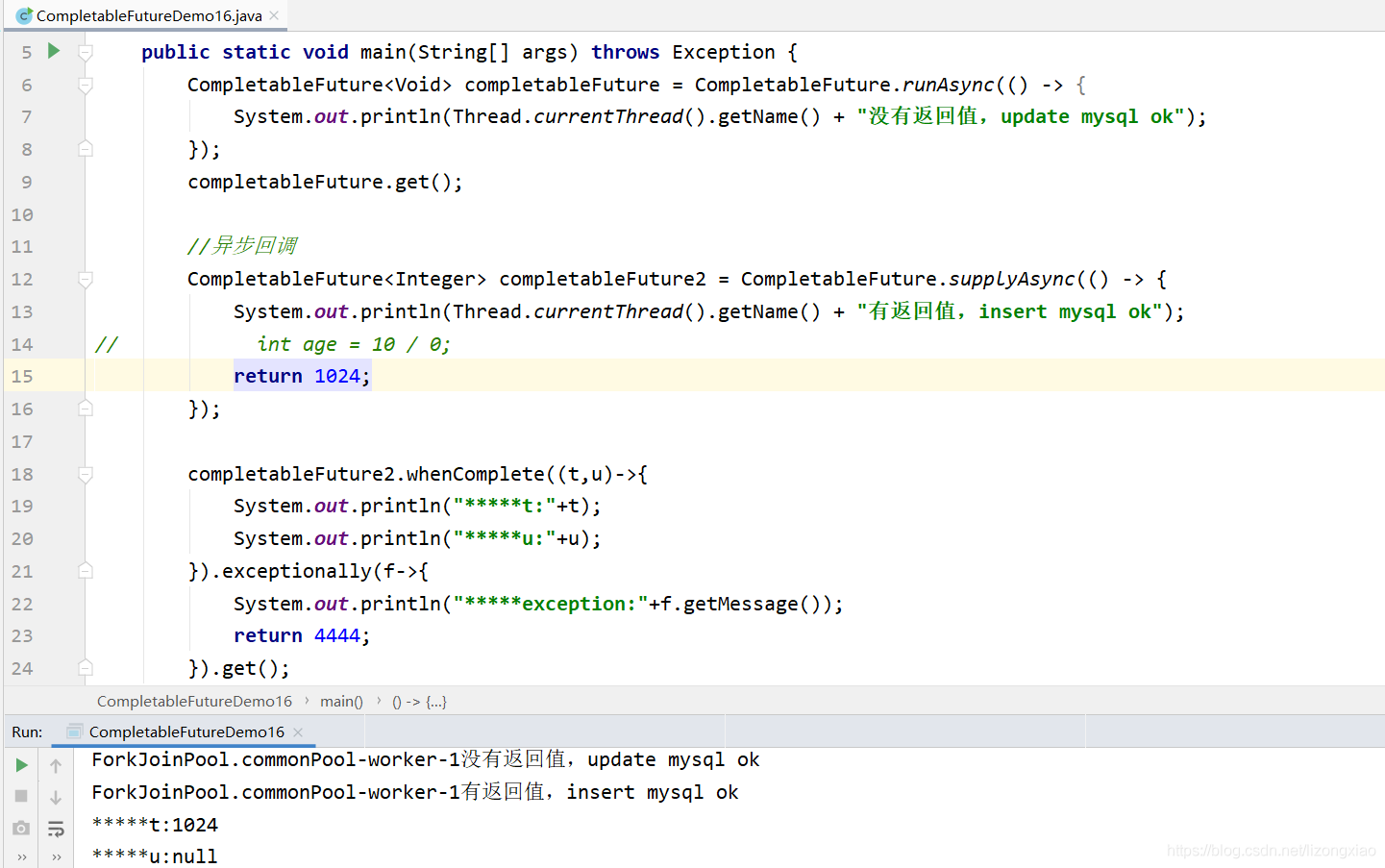
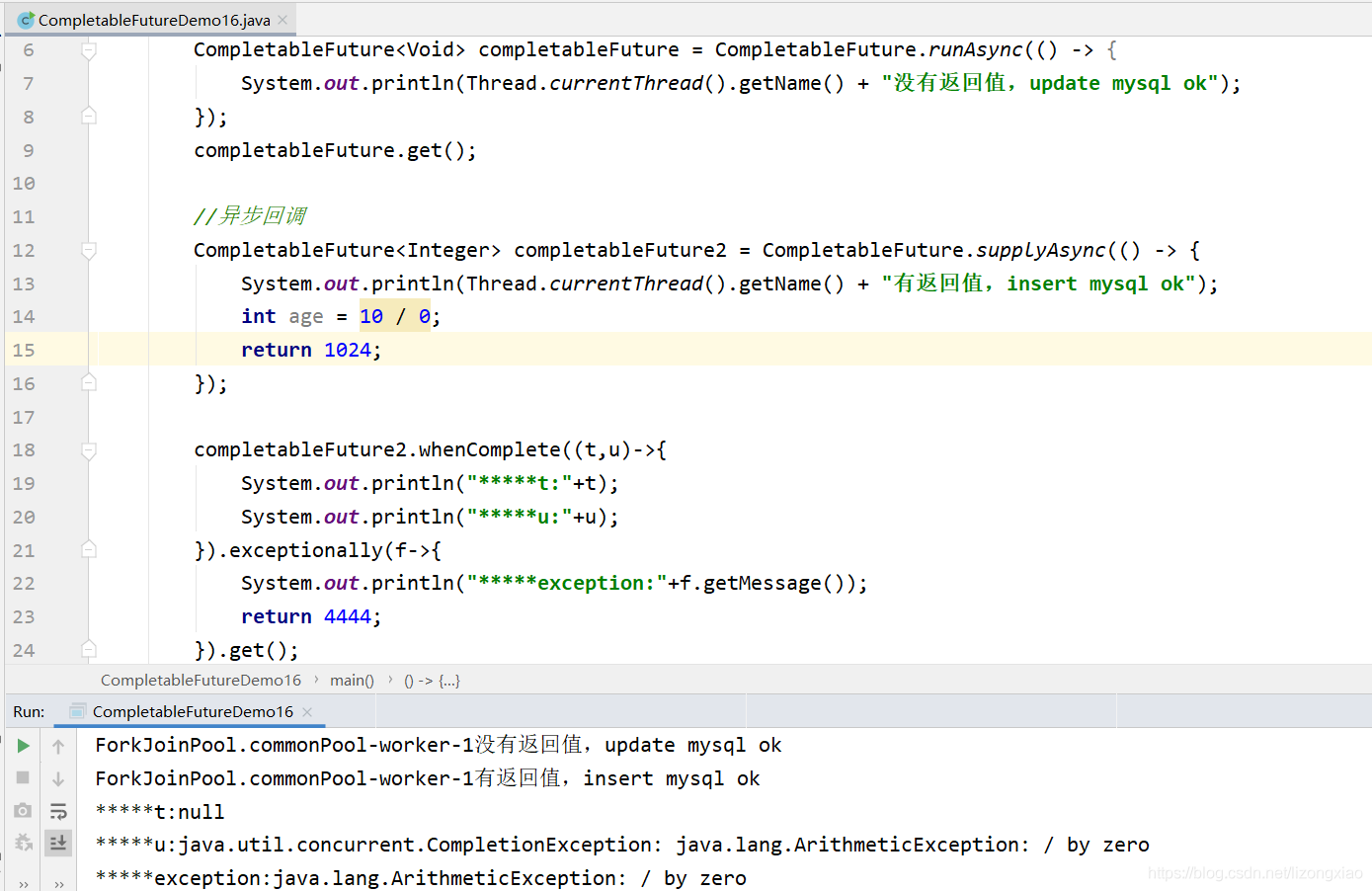
CompletableFuture异步回调 完结撒花
Others: